NCERT SOLUTIONS
Chapter 2 : Acids, Bases and Salts
Intext Questions
Page No.18
1. You have been provided with test three test tubes. One of them contains distilled water and the other two contain an acidic solution and a basic solution respectively. If you are given only red litmus paper. How will you identify the contents of each test tube ?
Ans: We will put the red litmus in all the three tubes turn by turn. The solution which turns red litmus to blue will be the basic solution. The blue litmus paper formed here can now be used to test the acidic solution. Now we put the blue litmus paper in the remainning two test tubes turn by turn. The solution which turns blue litmus paper to red will be the acidic solution. The solution which has no affect any litmus paper will be neutral and hence it will be distilled water.
Questions
Page No. 22
1. Why should curd and sour substance not be kept in brass and copper vessels ?
Ans: Curd and sour substances should not be kept in brass and Copper vessels because curd and other sour food stuffs contain acids which can react with the metal of the vessels to form poisonous metal compounds which can cause food poisoning and affect our health adversely.
2. Which gas is usually liberated when an acid reacts with a metal? Illustrate with an example. How will you test for the presence of this gas ?
Ans: Hydrogen gas is liberated when acid reacts with metal. The reaction involved is
H2SO4 (aq) + Zn(s) → ZnSO4 (aq) + H2(g)
Experiment: The Experimental setup for this experiment is shown in the figure below:
At first, we take 5 ml of dilute sulphuric acid in the test tube and add a few of zinc granules to it, we observe that as soon as the reaction between zinc and dilute sulphuric acid starts and hydrogen gas is evolved in the test tube and through the delivery tube it is passed through the soap solution and bubbles are formed in the soap solution.
We take a burning candle near the soap bubble filled with gas, we observed that the bubble burst and hydrogen gas burn with a pop sound.
3. Metal compound A reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid to produce effervesence. The gas evolved extinguishes a burning candle. write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction if one of the compound formed is calcium chloride.
Ans: As the Metal compound released is calcuim chloride, so the gas evolved is carbon dioxide (CO₂). Hence the metal A should be calcuim carbonate. Hence the reaction between calcuim carbonate and dilute Hydrochloric acid is
CaCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) → CO2(g) + CaCl2(aq) +2H2O(l)
Questions
Page No. 25
1. Why do HCl, HNO3 show acidic characters. is aqueous solution while solutions of compounds like alcohol and glucose do not show acidic character ?
Ans: HCl, HNO3 etc. give H+ ions in aqueous solution. On the other hand alcohol and glucose don’t give H+ ions in aqueous solution. That is why HCl, HNO3 etc. Show acidic characters in aqueous solutions while solutions of compounds like alcohol and glucose character do not show acidic character.
2. Why does an aqueous solution of an acid conduct electricity ?
Ans: An aqueous solution of an acid conduct electricity because of the H+ ions Produced in aqueous solution.
3. Why does dry HCl gas do not change the colour of the dry litmus paper ?
Ans: Dry HCl gas does not give H+ ions and therefore does not change the colour of dry litmus paper.
4. While diluting an acid, why is it recommended that the acid should be added to water and not water to the acid ?
Ans: Reaction of acid with water is a highly exothermic. If water is added to a concentrated acid, the heat generated may cause the mixture to splash out and cause burns. On the other hand if acid is added to water, the heat generated will be absorbed by the water. That is why While diluting an acid, it is recommended that the acid should be added to water and not water to the acid.
5. How is the concentration of hydronium ions (H2O+) affected when a solution of an acid is diluted ?
Ans: When a given amount of an acid is added to water, there is a fixed number of hydronium ions per unit volume of the solution. On dilution, the number of hydronium ions per volume decreases and so concentration decreases.
6. How is the concentration of hydroxide ions (OH–) affected when excess base is dissolved in a solution of sodium hydroxide ?
Ans: The concentration of hydroxide ions (OH–) will increase when excess base is dissolved in a solution of sodium hydroxide but it happens to a limited extent only after which concentration become almost constant.
Questions
Page No. 28
1. You have to to solutions, A and B. The pH of solution A is 6 and pH of solution B is 8. Which solution has more hydrogen ions concentration? Which of this is acidic and which one is basic ?
Ans: The solution A has more hydrogen ion concentration than the solution B. So, A is acidic and B is basic.
2. What effect does the concentration of H+(aq) ions have on the nature of the solution ?
Ans: The concentration of H+(aq) ions is greater in the solution then the solution will be acidic in nature but if the concentration of H+(aq) ions is less then the solution will be basic in nature.
3. Do basic solutions also have H+(aq) ions ? If yes then why are these basic ?
Ans: Basic solutions have H+(aq) ions.
In basic solutions the number of hydronium ions (H+) is less than that of hydroxide ion (OH–). That is why inspite of having hydronium ions they are basic.
4. Under what soil condition do you think a farmer would treat the soil of his fields with quick lime (calcium oxide) or slaked lime (Calcium hydroxide) or chalk (calcium carbonate) ?
Ans: If the soil of the fields becomes acidic then the farmer would treat the soil of his field with quick lime or slaked lime or chalk.
Questions
Page No. 33
1. What is the common name of the compound CaOCl2 ?
Ans: Bleaching powder.
2. Name the substance which on treatment with chlorine yields bleaching powder.
Ans: Calcium Hydroxide [Ca(OH)2]
3. Name the sodium compound which is used for softening hard water.
Ans: Washing soda (Sodium Corbonate)
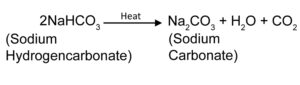
4. What will happen if a solution of sodium hydrocarbonate is heated ? Give the equation of the reaction involved ?
Ans: If a solution of Sodium hydrocarbonate is heated it will form Sodium Carbonate, water and carbon dioxide.
The reaction involved is
5. Write an equation to show the reaction between Plaster of Paris and water.
Ans: The reaction involved is
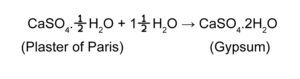
EXERCISES
1. A solution turns red litmus blue. its pH is likely to be (a) 1 (b) 4 (c) 5 (d) 10
Ans: (d) 10
2. A solution reacts to with crushed egg-shells to give a gas that turns lime-water milky. (a) NaCl b) HCl c) LiCl d) KCl
Ans: (b) HCl
3. 10 mL of a solution of NaOH is found to be completely neutralised by 8 ml of a given solution of HCI. If we take 20 ml of the same solution of NaOH the amount of HCl solution (the same solution as before) required to neutralise it will be
(a) 4 ml (b) 8 ml (c) 12 ml (d) 16 ml
Ans: (d) 16 ml
4. Which one of the following types of medicines is used for treating indigestion ? (a) Antibiotic (b) Analgesic (c) Antacid (d) Antiseptic
Ans: (c) Antacid
5. Write word equations and then balanced equations for the reaction taking place when
(a) dilute sulphuric acid reacts with fine granules.
Ans: The required word equations is
Dilute sulphuric acid + Zinc→ Zinc Sulphate + Hydrogen gas
The required balanced equation is
H2SO4 (aq) + Zn(s) →ZnSO4 (aq) + H2(g)
(b) dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with magnesium ribbon
Ans: The required word equations is
dilute hydrochloric acid + magnesium ribbon → magnesium chloride + Hydrogen gas
The required balanced equation is
2HCl(aq) + Mg(s) → MgCl2(aq) + H2(g)
(c) dilute sulphuric acid reacts with aluminium powder
Ans: The required word equation is
Dilute sulphuric acid + aluminium powder → aluminium sulphate + Hydrogen gas
The required balanced equation is
3H2SO4(aq) + 2Al(s) → Al2(SO4)3(aq) + 3H2(g)
(d) dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with iron filings
Ans: The required word equation is
Dilute hydrochloric acid + Iron filings → Iron chloride + Hydrogen gas
The required balanced equation is
6HCl(aq) + 3Fe(s) → 3FeCl3(aq) + 3H2(g)
6. Compounds such as alcohols and glucose also contain hydrogen but are not categorised as acids. Describe an activity to prove it.
Ans:
First we take solution of glucose, alcohol, hydrochloric acid, sulphuric acid etc and now fixed two nails on a cork and place the cork in a 100 ml beaker and connect the nails to the two terminals of a 6 volt battery through a bulb and a switch as shown in the figure above.Now we pour some dilute HCI in the beaker and switch on the current . Similarly by taking separately alcohol, glucose and sulphuric acid in the beaker and repeated experiments are done.
In the experiments we observe that in case of glucose and alcohol the bulb does not glow but in case of hydrochloric acid and sulphuric acid the bulb glows.
In case of acids the bulb glows because the aqueous solution of acids can produce hydrogen ions(H+) .On the other hand in case of glucose and alcohol the bulk does not glow because solution of them can not produce hydrogen ions which is responsible for the conduction current through them.From this experiment it is proved that inspite of having hydrogen alcohol and glucose are not catagorised as acids.
7. Why does distilled water not conduct electricity whereas rain water does ?
Ans: Distilled water does not conduct electricity because it does not contain any ionic compound like acid ,base or salts dissolved in it whereas rain water while falling to the earth through the atmosphere dissolve an acidic gas carbon dioxide from air and forms carbonic acid(H2CO3). Carbonic acid provide hydrogen ions, H+(aq) and carbonate ions, CO3-2 (aq) to rain water. Hence, due to the presence of carbonic acid which provides ions to rain the rain conducts electricity.
8. Why do acids not show acidic behaviour in the absence of water ?
Ans: Acidic behavior of acids is due to the Presence of hydrogen ions, H+(aq) in them. The acid produces hydrogen ions , H+(aq) in the presence of water. So, in the absence of water an acid will not show acidic behavior in in absence of water.
9. Five solutions A, B, C, D and E when tested with universal indicator showed pH 4,1,11,7 and 9 respectively.Which solution is.
(a) neutral?
(b) strongly alkaline ?
(c) strongly acidic ?
(d) weakly acidic ?
(e) weakly alkaline ?
Arrange the pH in increasing order of hydrogen ion concentration.
Ans: (a) D is Neutral.
(b) C is strongly alkaline.
(c) B is strongly acidic.
(d)A is weakly acidic.
(e) E is weakly alkaline.
In increasing order of hydrogen-ion concentration,
11<9<7<4<1
i,e C<B<D<A<B
10. Equal lengths of magnesium ribbons are taken in test tubes A and B .Hydrochloric acid (HCI) is added to test tube A, while acetic acid(CH3COOH) is added to test tube B.Amount and concentration taken for both the acids are same. In which test tube will the fizzing occur more vigorously and why?
Ans: Fizzing will occur more vigorously in the test tube A. Hydrochloric acid (HCI) is a strong acid whereas acetic acid(CH3COOH) is a weak acid Being strong acid hydrochloric acid strongly reacts with magna magnesium ribbon in comparison with the acetic acid to produce more hydrogen gas.That is why in the test tube A vigorously fizzing will occur more vigorously.
11.Fresh milk has a pH of 6.How do you think the pH will change as it turns into curd ? Explain your answer .
Ans: pH of milk falls below 6 as it turns into curd due to the formation of lactic acid during this process lactic acid present in it reduce its pH value.
12. A milkman adds a very small amount of baking soda to fresh milk.
(a) Why does he shift the pH of the fresh milk from 6 to slightly alkaline.
(b) Why does this milk take a Long time to set as curd .
Ans: (a) Milk is made slightly alkaline so that it may not get sour easily due to the formation of lactic acid in it.
( b) The alkaline milk takes a longer time to set as curd because the lactic acid being formed has to first neutralise the alkali present in it.
13. Plaster of Paris should be stored in a moisture – proof container. Explain why ?
Ans: Plaster of paris should be stored in moisture proof container because in presence of moisture it changes to gypsum. This will make the plaster of paris useless after sometime. That is why plaster of paris should be stored in a moisture proof container.
14. What is a neutratisation reaction? Give two examples.
Ans: The reaction between an acid and a base to give a salt and water is called a neutratisation reaction.
Examples: (i) NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H₂O(l)
(ii) H2SO4(aq) +NaOH(aq) → Na2SO4(aq) + 2H2O(l)
15. Give two important uses of washing soda and baking soda.
Ans: Uses of washing soda are
(i) It is used as a cleaning agent for domestic purposes.
(ii) It is used for removing permanent hardness of water.
Uses of baking soda are
(i) It is used as an ingredient in antacids.
(ii) It is used in soda- acid fire extinguishers.
Additional Questions
1. What are Acids ?
Ans :The substances which are sour in taste and change the colour of blue litmus to red are called acids.
Example : Hydrochloric acid (HCl), Sulphuric acid (H₂SO4) etc.
2. What are Bases ?
Ans: The substances which are bitter in taste and changes the colour of the red ritmus to blue are called bases.
Example :Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH),Calcium Hydroxide Ca(OH)2
3. What is litmus ?
Ans: Litmus is a natural indicator which is extracted from lichen.
It is found in two types:
(i)Litmus paper and (ii) Litmus solution.
(i)Litmus paper :It is found in two colour namely blue litmus paper and red litmus paper.
(ii) Litmus solution : It is a purple dye.
4. What are indicators ?
Ans: The substances which change in colour and smell in acidic or basic medium are called indicators.
Indicators are of two types:
(i)Natural indicators: Litmus, turmeric,red cabbage leaves etc.
(ii) Synthetic indicators :Methyl orange phenolphthalein etc.
5. What are olfactory indicators ?
Ans: The substances whose odour changes in acidic or basic medium are called olfactary indicators.
Example : Vanilla, onion and clove etc .
6. How do acids and bases react with metals?
Ans: When acids react with metal,it produces salt and hydrogen gas.
The required word equation is
Acid + Metal → Salt + Hydrogen gas
Example : Zn(s) +) HCl(aq) → ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g)
When bases react with metal it also produces salt and hydrogen gas.
The required word equation is
Base + Metal → Salt + Hydrogen gas
Example : 2NaOH(aq) +Zn(s) → Na2ZnO2(aq) + H2(g)
7. How do metal carbonates and metal hydrogen carbonates react with acids?
Ans: Metal carbonates and metal hydrogen carbonates react with acids to produce salts,
carbon dioxide and water.
The required word equation is
Metal carbonate / Metal hydrogen carbonates + Acid → Salt + Carbon dioxide + water
Example : Na2CO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) → 2NaCl(aq) +CO2(g) + H₂O(l)
NaHCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) → 2NaCl(aq) +CO2(g) + H₂O(l)
8. What is salt ?
Ans: In neutralisation reaction, the new Product is formed along with water is called salt.
Example: NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H₂O(l)
Here, Sodium chloride (NaCl) is the salt.
9. How do metallic oxides react with acid ?
Ans: Metallic oxides react with acids to produce salt and water.
Metallic Oxides are basic in nature.
The required word equation is
Metal oxide + Acid → Salt + Water
Example: CuO(aq) + HCl(aq) → CuCl2(aq) + H2O(l)
10. Why are metallic oxides basic in nature ?
Ans: As metallic oxides react with acids to product salt and water, Similar to the reaction of a base with an acid.That is why metallic oxides are basic in nature.
11. How do non-metallic oxides reacts with base ?
Ans: Non-metalic oxides react with base to produce salt and water.
Non-metallic oxides are acidic in nature.
Example: CO2(g) + Ca(OH)2(aq) → CaCO3(aq) + H2O(l)
12. Why are non-metallic oxides are acidic in nature ?
Ans: As non-metallic oxides react with base to produce salt and water, Similar to the reaction of a acid with base . That is why non-metallic oxides are acidic in nature.
13. What do all acids and all bases have in Common?
Ans: All acids and all bases have the following common properties:
(i) In aqueous Solution both acid and base produce ions.
(ii) Due to the ions produced in the aqueous Solution both acid and base can conduct current.
14. What happens to an acid or a base in a water solution ?
Ans: In water solution acid produces hydronium ion(H+) or (H3O+).
Example: HCl + H2O → H3O++ Cl–
In water solution, bases produce hydroxide ion(OH–).
Example : NaOH(s)+ H2O → Na+(aq) + (OH–)
15. What is an alkali? Give examples.
Ans: The base which is soluble in water is called an alkali .
Example: Soduim hydroxide (NaOH), calcium hydroxide [Ca(OH)2] and potassium hydroxide (KOH) are some examples of alkali.
16. What is pH scale ?
Ans: A scale for measuring hydrogen ion concentration in a solution is called pH scale.
On the pH scale we can measure pH generally from 0 to 14. Higher the hydronium ion concentration lower is the pH value.
Note: (i) pH of a neutral solution is 7.
(ii) Values less than 7 on the pH scale represent an acidic solution.
17. What are strong acids ? Give examples.
Ans: Acids that give rise to more H+ ions are said to be strong acids.
Example: Hydrochloric acid (HCl) ,Sulphuric acid (H2SO4) etc.
18. What are weak acids ?
Ans: Acids that give less H+ ions are said to be weak acids.
Example: Acetic acid(CH₃COOH),tartaric acid etc.
19. What is the working pH limit of our body ?
Ans: Our body work within the pH range of 7.0 to 7.8 .
20. What is acid rain ?
Ans: When pH of rain water is less than 5.6, it is called acid rain.
21. When does tooth start decay ?
Ans: Tooth decay starts when the pH of the mouth is lower than 5.5 .
22. What is milk of magnesium ?
Ans: Magnesium hydroxide [Mg(OH)2] is called milk of magnesium.
It is used as antacid
23. What is rock salt ?
Ans: Rock salt is a salt consisting of sodium chloride and is found as large crystals which is brown in colour due to impurities present in it.
Rock salt s mined like coal.
24. What is brine ?
Ans: An aqueous solution of sodium chloride is called brine.
25. What is chlor- akali process ?
Ans: when electricity is passed through an aqueous solution of sodium chloride (called brine) it decomposes to form sodium hydroxide. The proces is called the chlor – alkali process.
The reaction involved is
2NaCl(aq) + 2H₂O(l) → 2NaOH(aq) + Cl2(g) + H2(g)
26. What is bleaching powder ? Give some uses of it.
Ans: Bleaching powder is a white colour powder which is produced by the action of chlorine on dry slaked lime, Ca(OH)2.
The chemical formula of bleaching powder is CaOCl2
The reaction involved is
Ca(OH)2 + Cl2 → CaOCl2 + H₂
Uses of bleaching power:
(i) Bleaching powder is used for bleaching cotton and linen in the textile industry, for bleaching wood pulp in paper factories and for bleaching washed clothes in laundry.
(ii) It is used as an oxidising agent in many chemical industries.
(iii)It is used for disinfecting drinking water to free of germs.
27. What is baking soda ? Give some uses of it .
Ans: Sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO3) is known as Baking Soda.
It is produced by the reaction of sodium chloride, water, carbon dioxide and ammonia.
The reaction involved is
NaCl + H2O + CO2 + NH3 → NH4Cl + NaHCO3
( Ammonium (Sodium
chloride) hydrogencarbonate)
The uses of baking soda:
(i) It is used for making baking powder.
(ii) It is also used as an ingredient in antacids.
(iii) It is also used in soda-acid fire extinguishers.
28. What is washing soda ?
Ans: Sodium carbonate having 10 water molecules as water of crystallization is called washing soda.
The chemical formula of washing soda is Na2CO3.10H2O .
It is produced by the crystallisation of sodium carbonate.
The chemical reaction involved is
Na2CO3 + 10H2O → Na2CO3.10H2O.
(Sodium
carbonate)
Uses of washing soda:
(i) It is used in glass, soap and paper industries.
(ii) It is reed in the manufacture of sodium compounds such as borax.
(iii) It is used as a cleaning agent for domestic purposes.
(iv) It is used for removing permanent hardness of water.
29. What is crystallisation of water ? Give examples.
Ans: Water of crystallisation is the fixed number of water molecules present in one formula to unit of a salt.
Example: Fire water molecules are present in one formula unit of copper sulphate, (CuSO4 .5H20).
Ten water molecules are present in one formula unit of washing Soda, Na2CO3.10H20
30. What is plaster of paris ? Give some uses of it .
Ans: Calcium sulphate hemihydrate is called plaster of paris .
It is a white powder and the chemical formula of it is CaSO4½ H₂O.
On heating gypsum at 373 K it loses water molecules and becomes cats calcium sulphate hemihydrate or plaster of paris.
Uses of plaster of paris:
(i) It is used by doctors as plaster for supporting fractured bones in the right position.
(ii) It is used for making toys, materials for decoration and for making surfaces smooth .
31. What is gypsum ?
Ans: Calcium sulphate having two water molecules as water of crystallisation is called gypsum.
The chemical formula of it is CaSO4.2H2O.
When plaster of paris reacts with water, it changes to gypsum.
The chemical reaction involved is
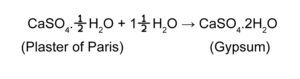
![]()
0 Comments